Current issue
Online First
Archive
Instructions for Authors
Guide for Authors
Peer Review Policy
Research Ethics Policy
Crossmark Policy
Ghostwriting and Guest Authorship
Copyright
Open Access Policy
Plagiarism
About the Journal
Aim and Scope
Scientific Board
Publisher
Editorial Board
Indexing in Databases
Personal Data Protection
Repository Policy
Contact
ORIGINAL PAPER
The Influence of Flow Rate on CIP Cleaning Efficiency and Flow Resistance in an Installation with a Three-Section PHE
1
Łukasiewicz Research Network - Poznan Institute of Technology, Poznań, Poland
2
Poznań University of Technology, Poznań, Poland
3
Koszalin University of Technology, Department of Mechanical and Power Engineering, Division of Food Industry Processes and Facilities, Poland
Submission date: 2025-05-29
Acceptance date: 2025-07-08
Online publication date: 2025-07-09
Corresponding author
Maksymilian Galiński
Centrum Zrównoważonej Gospodarki, Sieć Badawcza Łukasiewicz - Poznański Instytut Technologiczny, ul. Ewarysta Estkowskiego 6, 61-755, Poznań, Poland
Centrum Zrównoważonej Gospodarki, Sieć Badawcza Łukasiewicz - Poznański Instytut Technologiczny, ul. Ewarysta Estkowskiego 6, 61-755, Poznań, Poland
Journal of Research and Applications in Agricultural Engineering 2025;70(1)
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
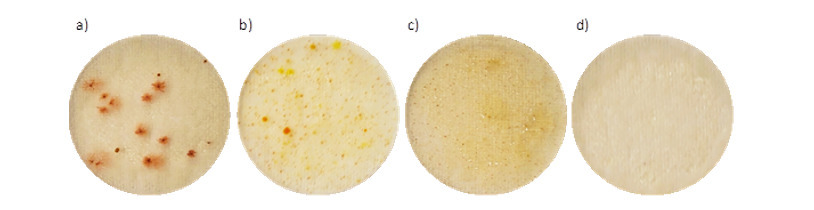
Due to the widespread application of plate heat exchangers (PHE) in the food industry, a key aspect of their operation is ensuring a high level of hygiene, which guarantees the microbiological cleanliness of the final product. This is achieved through the cleaning of installations containing PHE using the Clean-in-Place (CIP) system. An important aspect is the determination of flow resistance, as this enables the specification of drive parameters and the selection of a pump that provides a sufficiently high flow rate through the installation, particularly required during the pre-rinsing stage.
The subject of the research was a three-section plate heat exchanger, which forms part of a prototype technological line designed for the pasteurisation of liquid egg mass and its fractions – egg white and yolk. As part of the study, the effectiveness of the cleaning process was assessed depending on the flow rate. Based on experimental results, the minimum flow rate necessary for effective cleaning using commercial sodium hydroxide (NaOH)-based cleaning agents was determined. In addition, the extent to which the relationship described in the literature – linking flow rate with hydraulic resistance in PHE – is confirmed under real operating conditions during the cleaning process in the CIP system was analysed. The results obtained may be used to optimise the parameters of the CIP process, which will contribute to increased efficiency, reduced consumption of chemical agents, and improved microbiological safety of the final product.
REFERENCES (22)
1.
K. Maziarz et al., ‘Analysis of Haze Susceptibility in Beers with Unmalted Barley Addition Under Varying Storage Conditions’, Journal of Research and Applications in Agricultural Engineering, vol. 68, no. 2, Nov. 2023, doi: 10.53502/siwc4991.
2.
J. Diakun, S. Mierzejewska, and J. Przepiórka, ‘Monitorowanie parametrów czynnika myjącego w trakcie mycia w przepływie’, Postępy Techniki Przetwórstwa Spożywczego, vol. 1, pp. 34–36, 2009.
3.
O. Arsenyeva, O. Matsegora, P. Kapustenko, A. Yuzbashyan, and J. Jaromír Klemeš, ‘The water fouling develop-ment in plate heat exchangers with plates of different corrugations geometry’, Thermal Science and Engineering Pro-gress, vol. 32, Jul. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.tsep.2022.101310.
4.
S. Brooks and R. Roy, ‘Design and complexity evaluation of a self-cleaning heat exchanger’, Int J Heat Mass Transf, vol. 191, Aug. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2022.122725.
5.
C. Spiegel, F. Aselmeyer, W. Augustin, and S. Scholl, ‘Quantification method for cleaning-in-place procedures in micro structured equipment’, Food and Bioproducts Processing, vol. 134, pp. 150–162, Jul. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.fbp.2022.05.010.
6.
A. L. Bowler, S. Rodgers, D. J. Cook, and N. J. Watson, ‘Bayesian and ultrasonic sensor aided multi-objective opti-misation for sustainable clean-in-place processes’, Food and Bioproducts Processing, vol. 141, pp. 23–35, Sep. 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.fbp.2023.06.010.
7.
L. Beckedorff, R. P. P. da Silva, G. S. M. Martins, K. V. de Paiva, J. L. G. Oliveira, and A. A. M. Oliveira, ‘Flow maldis-tribution and heat transfer characteristics in plate and shell heat exchangers’, Int J Heat Mass Transf, vol. 195, Oct. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2022.123182.
8.
H. Jouhara, N. Khordehgah, S. Almahmoud, B. Delpech, A. Chauhan, and S. A. Tassou, ‘Waste heat recovery tech-nologies and applications’, Jun. 01, 2018, Elsevier Ltd. doi: 10.1016/j.tsep.2018.04.017.
9.
A. Durmuş, H. Benli, I. Kurtbaş, and H. Gül, ‘Investigation of heat transfer and pressure drop in plate heat ex-changers having different surface profiles’, Int J Heat Mass Transf, vol. 52, no. 5–6, pp. 1451–1457, Feb. 2009, doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2008.07.052.
10.
P. Kapustenko, J. J. Klemeš, O. Arsenyeva, and L. Tovazhnyanskyy, ‘PHE (Plate Heat Exchanger) for Condensing Duties: Recent Advances and Future Prospects’, Jan. 01, 2023, MDPI. doi: 10.3390/en16010524.
11.
A. Kumar Rai, V. Sachan, O. Mohammed Ismael, and H. Mahdi, ‘AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF HEAT TRANSFER IN A PLATE HEAT EXCHANGER’, IJARET, 2014. [Online]. Available: www.iaeme.com/ijaret.asp.
12.
C. Gulenoglu, F. Akturk, S. Aradag, N. Sezer Uzol, and S. Kakac, ‘Experimental comparison of performances of three different plates for gasketed plate heat exchangers’, International Journal of Thermal Sciences, vol. 75, pp. 249–256, Jan. 2014, doi: 10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2013.06.012.
13.
M. A. H. Mudhafar, ‘Numerical study of two-phase flow in multi-channels plate heat exchanger’, International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, vol. 138, Nov. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2022.106380.
15.
D. A. . Seiberling, Clean-in-place for biopharmaceutical processes. Informa Healthcare, 2008.
16.
Z. Kowalczuk and M. S. Tatara, ‘Improved model of isothermal and incompressible fluid flow in pipelines versus the Darcy-Weisbach equation and the issue of friction factor’, J Fluid Mech, vol. 891, 2020, doi: 10.1017/jfm.2020.131.
17.
Jaćimović. Nikola, M. Stamenić, and P. Kolendić, ‘A Novel Method for the Inclusion of Pipe Roughness in the Ha-zen- Williams Equation’, FME Transactions, vol. 43, no. 1, pp. 40–46, 2015, doi: 10.5937/fmet1501040S.
18.
T. Hobler, Inżynieria chemiczna Ruch ciepła i wymienniki. Warszawa: Państwowe Wydawnictwo Techniczne, 1959.
19.
A. A. Neagu, C. I. Koncsag, A. Barbulescu, and E. Botez, ‘Estimation of pressure drop in gasket plate heat exchang-ers’, Ovidius University Annals of Chemistry, vol. 27, no. 1, pp. 62–72, Jun. 2016, doi: 10.1515/auoc-2016-0011.
20.
S. Gusew and R. Stuke, ‘Pressure Drop in Plate Heat Exchangers for Single-Phase Convection in Turbulent Flow Regime: Experiment and Theory’, International Journal of Chemical Engineering, vol. 2019, 2019, doi: 10.1155/2019/3693657.
21.
F. A. S. Mota, E. P. Carvalho, and M. A. S. S. Ravagnani, ‘Modeling and Design of Plate Heat Exchanger’, in Heat Transfer Studies and Applications, 2015, pp. 165–199.
22.
S. Mohebbi and F. Veysi, ‘Numerical investigation of small plate heat exchangers performance having different surface profiles’, Appl Therm Eng, vol. 188, Apr. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2021.116616.
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.